Useful information for pumps

Antlies-pumps
Pump categories
Centrifugal pump
What is a centrifugal pump?
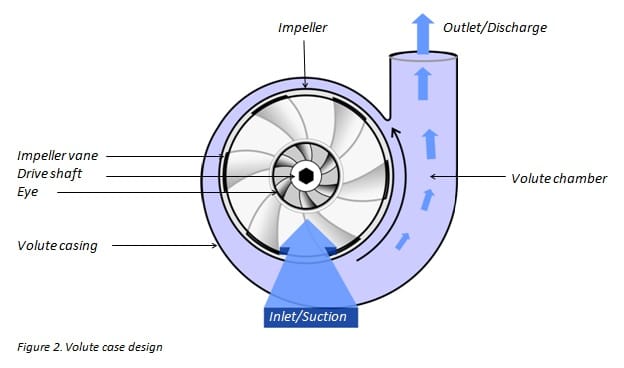
A centrifugal pump is a mechanical device designed to move a fluid by transferring rotational energy from one or more driven motors, called impellers. The fluid enters the rapidly rotating impeller along its axis and is discharged by centrifugal force along its circumference through the ends of the impeller blades. The action of the blade increases the speed and pressure of the fluid and also directs it towards the pump outlet. The pump housing is specially designed to clamp the fluid from the pump inlet, direct it to the impeller and then decelerate and control the fluid before draining.
How does a centrifugal pump work?
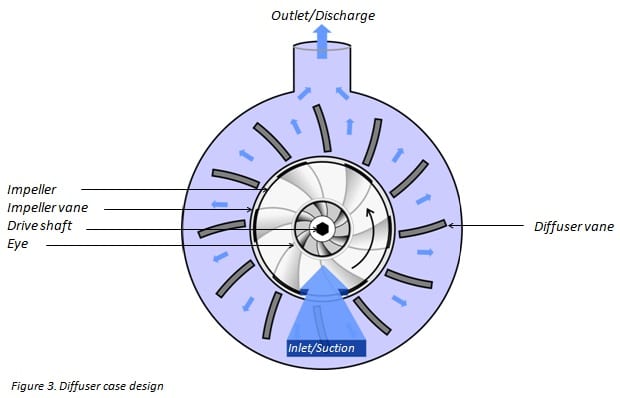
The impeller is the main component of a centrifugal pump. It consists of a series of convex fins. These are normally sandwiches between two disks (a closed impeller). For liquids with drift solids, an open or semi-open impeller (supported by a disc) is preferred (Figure 1). 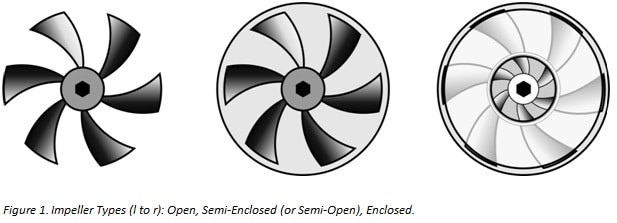
What are the main features of a centrifugal pump?
There are two main families of pumps: centrifugal and positive pumps displacement . Compared to the latter, centrifugal pumps are typically designed for higher flows and for pumping liquids of lower viscosity, up to 0,1 cP. In some chemical plants, 90% of the pumps used will be centrifugal pumps. However, there are some applications for which positive displacement pumps are preferred.
What are the limitations of a centrifugal pump?
The efficient operation of a centrifugal pump is based on the constant, high speed of rotation of the impeller. With high viscosity feeds, centrifugal pumps become increasingly inefficient: there is more resistance and more pressure is required to maintain a certain flow rate. In general, centrifugal pumps are suitable for applications of low pressure, high capacity, pumping liquids with viscosities between 0,1 and 200 cP. Slurries such as mud or high viscosity oils can cause excessive wear and overheating causing damage and premature damage. Positive displacement pumps often operate at significantly lower speeds and are less prone to these problems. Any pumped medium that is sensitive to shear (separation of emulsions, slurries or biological fluids) can also be damaged by the high speed of the impeller centrifugal pump. In such cases, the lowest speed of a positive displacement pump is preferred. An additional limitation is that, unlike a positive displacement pump, a centrifugal pump can not provide suction when it is dry: it must first be injected with the pumped fluid. Therefore, centrifugal pumps are not suitable for any application where the supply is intermittent. In addition, if the supply pressure is variable, a centrifugal pump produces a variable flow. a positive displacement pump is not sensitive to changing pressures and will provide stable performance. Thus, in applications where precise dosing is required, a positive displacement pump is preferred. The following table summarizes the differences between centrifugal and positive displacement pumps. Pump comparison: Centrifugal versus positive displacement
| Property | Centrifugal | Positive Shift |
| Effective viscosity range | Efficiency decreases with increasing viscosity (maximum 200 Cp) | Efficiency increases with increasing viscosity |
| Resistance to pressure | The flow varies depending on the changing pressure | The flow is not sensitive to pressure changes |
| Efficiency decreases at both higher and lower pressures | Efficiency increases with increasing pressure | |
| Trigger | Required | Not required |
| Flow (at constant pressure) | Continuous | Pulsing |
| Shear (separation of emulsions, pulps, biological fluids, food) | High speed damages the shear sensitive media | Low internal speed. Ideal for pumping fluids sensitive to shear |
What are the main applications for centrifugal pumps?
Centrifugal pumps are commonly used to pump water, solvents, organics, oils, acids, bases and any "fine" liquids in industrial, agricultural and domestic applications. In fact, there is a centrifugal pump design suitable for almost any application involving low viscosity fluids.
| Type of centrifugal pump | Application | Specifications |
| Canned motor pumps | Hydrocarbons, chemicals that are not allowed to leak | Sealless; impeller directly connected to the motor rotor. wetted parts contained in a container |
| Magnetic drive pump | Sealless; impeller driven by narrow coupled magnets | |
| Cutting / cutting pump | Wastewater in industry, chemical industry and food processing / sewage | Pulley equipped with grinding teeth for cutting solids |
| Circulating pump | Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning | Compact design |
| Multistage pump | High pressure applications | Multiple impellers for increased discharge pressures |
| Cryogenic pump | Liquid gas, refrigerants | Special building materials to tolerate low temperatures |
| Waste pump | Waste from mines, pits, construction sites | Designed to pump water containing solid residues |
| Manure pump | Mining, mineral processing, industrial pulps | Designed to handle and withstand very abrasive pulps |
Summary
A centrifugal pump operates by transferring rotational energy from one or more driven motors, called impellers. The action of the impeller increases the speed and pressure of the fluid and directs it to the outlet of the pump. With its simple design, the centrifugal pump is understandable and easy to operate and maintain
1 result
-
Gasoline Pumps (1)
-
Electric Surface Pumps (1)
-
Fountain pumps (1)
-
Special Pumps (1)
-
Pressure Pump Parts (1)
-
Oil-Wine-Milk-Oil Surface (1)
-
Pressure Groups (1)
-
Electric Submersible Pumps (1)
-
NAKAYAMA SP9700 PETROL PUMP 4 YEARS SP9700 017172
99.00 €
78.83 € Excluding VAT
97.75 € Includes VATNAKAYAMA SP9700 PETROL PUMP 4 YEARS SP9700 017172
4-year-old engine
Nakayama OHV
Power 2.5hp
Cubic capacity 97cc
Maximum Flow 200L / min
Manometric 12m
Nozzle Ø1 ”½ χ1” ½Out of stock